Solar DLM
ATTENTION! Everything on this page is work in progress and not yet verified!
Intro
Solar DLM is an extension of the DLM algorithm specifically developed for charging stations in combination with PV systems. Individual charging points or networks of charging points (DLM networks) can be connected to PV systems, allowing the generated solar power to be used for charging. An external energy management system is not required for the application.
When using Solar DLM, three different charging modes can be selected to determine the behavior of the charging points. These charging modes are Solar Surplus, Solar Charging, and Maximized Charging.
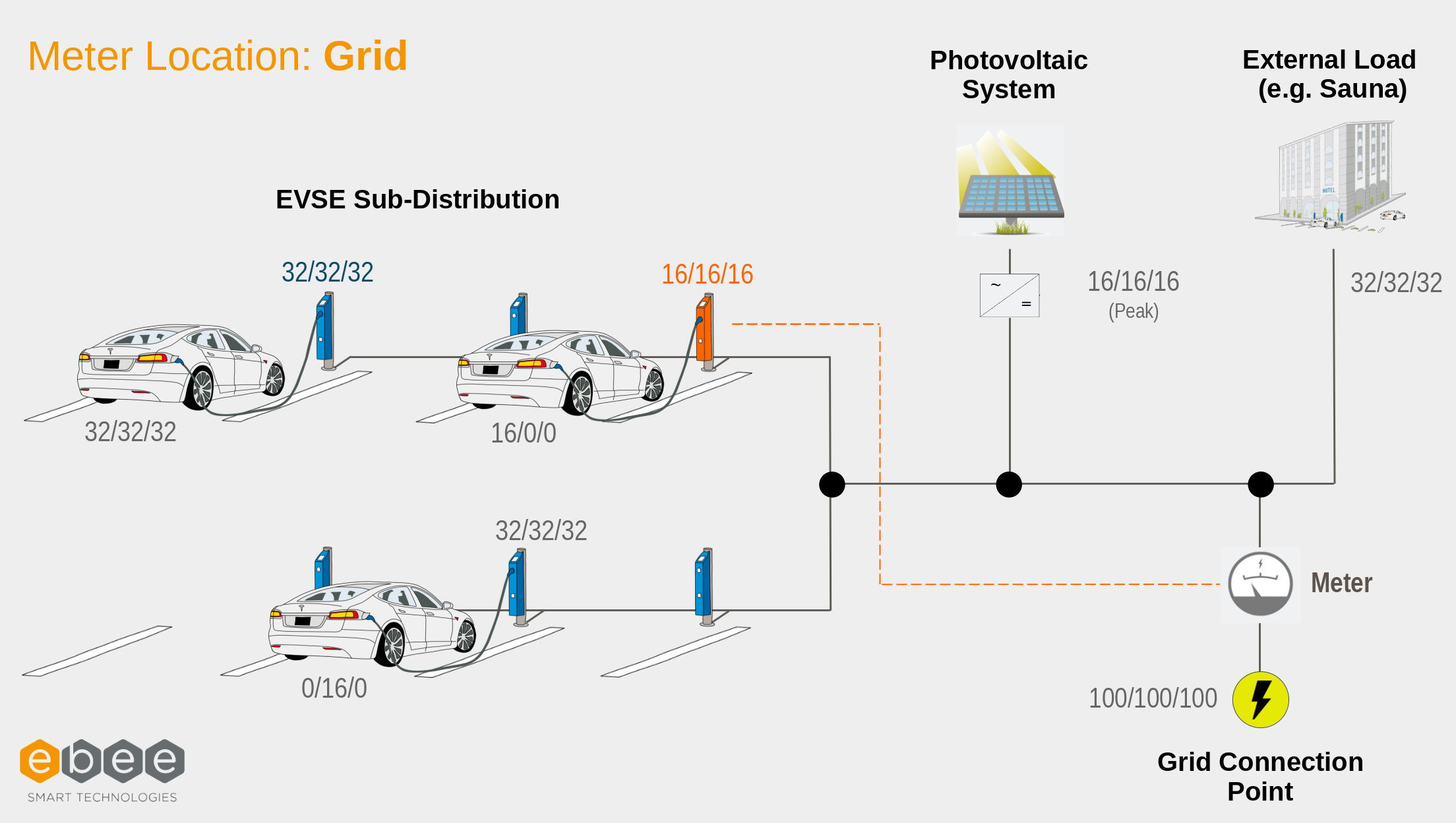
The available solar surplus is measured using an external meter within the installation. The external meter can be placed at two possible points: behind the PV system's inverter or at the grid connection point.
Automatic Phase Switching
The automatic phase switching feature optimizes the distribution of charging current during the charging process. During the charging process, individual phases can be switched on or off as needed. This makes it possible to continue charging even when the available power decreases.
Charging Modes
The distribution of available solar power can be configured according to demand. This makes it possible to control the percentage of grid supply during the charging process. This setting can be individually set for each vehicle, resulting in three different charging modes: Solar Surplus, Solar Charging, and Maximized Charging. Across all charging modes, it can be selected whether automatic phase switching should be active.
Solar Surplus
The Surplus Charging mode ensures that only the surplus power provided by a meter at the grid connection point or an inverter is used for charging. The charging current is regulated depending on the surplus power measured. If the measured power falls below the threshold of 1.4 kW, the charging process is paused.
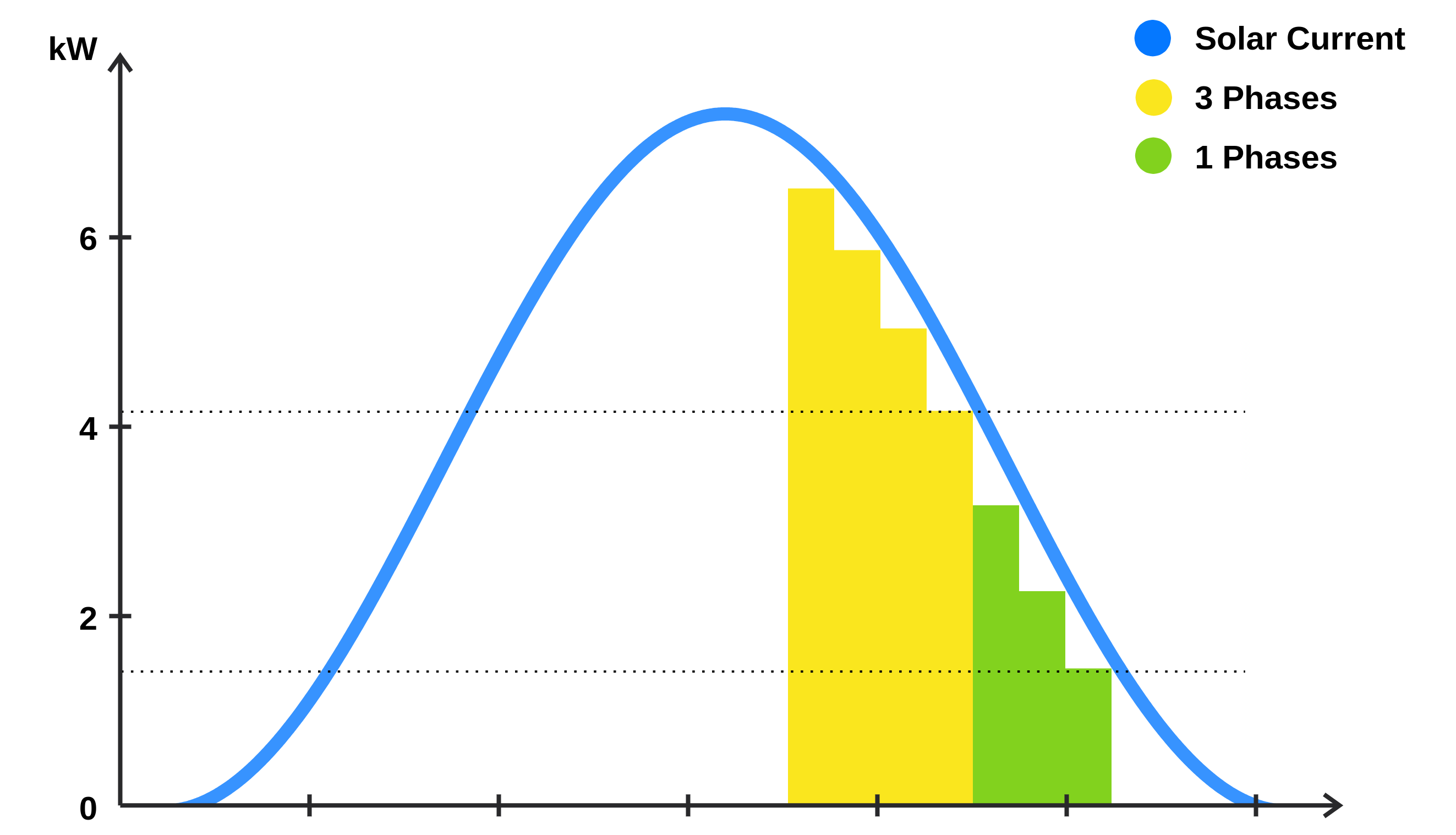
Solar Charging
The Surplus Charging mode ensures that mainly surplus power provided by a meter at the grid connection point or an inverter is used for charging. If the surplus is insufficient to reach the minimum charging power of 1.4 kW, the grid is used to fill the gap. Grid injection is thus avoided as much as possible.
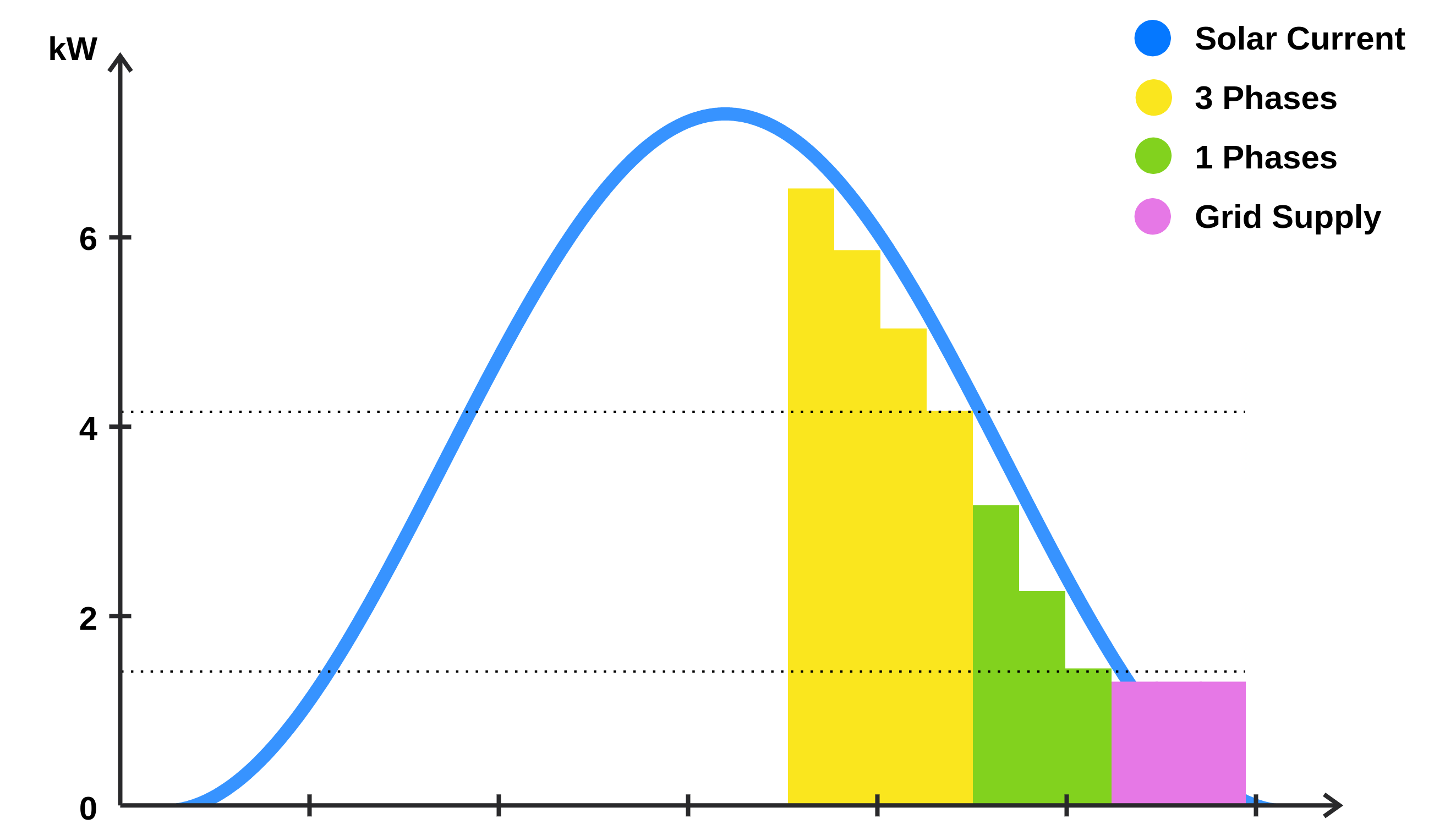
Maximized Charging
The Maximum Power mode ensures that the vehicle is charged as quickly as possible. The solar surplus is combined with grid power to charge all vehicles at maximum power.
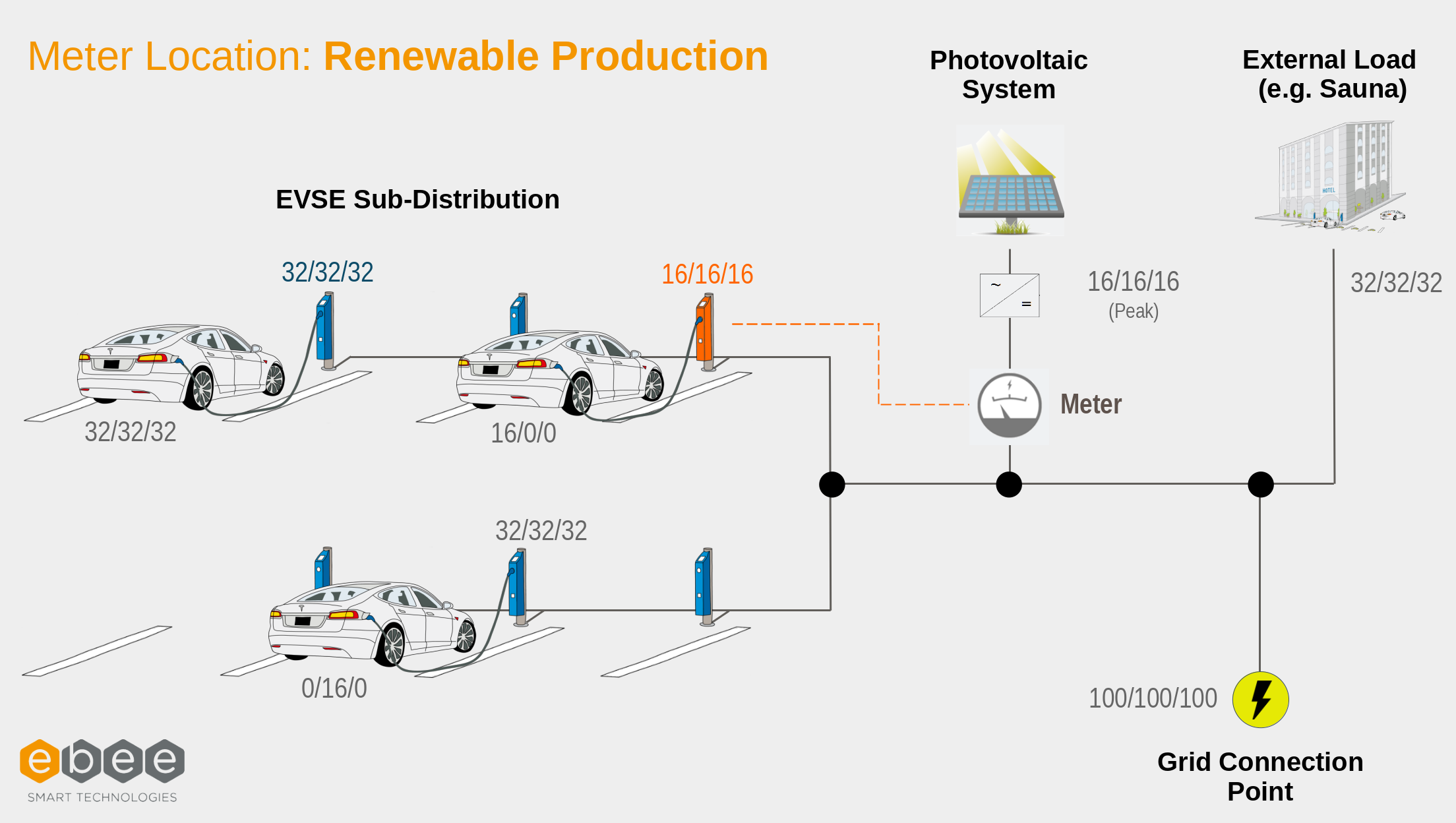
External Meter Locations
To distribute surplus solar energy to the charging points as needed, an external meter must be used. This external meter can be placed at two different locations in the installation: at the Renewable Production location and at the Grid location.
This results in two configurations, which are described in more detail below.
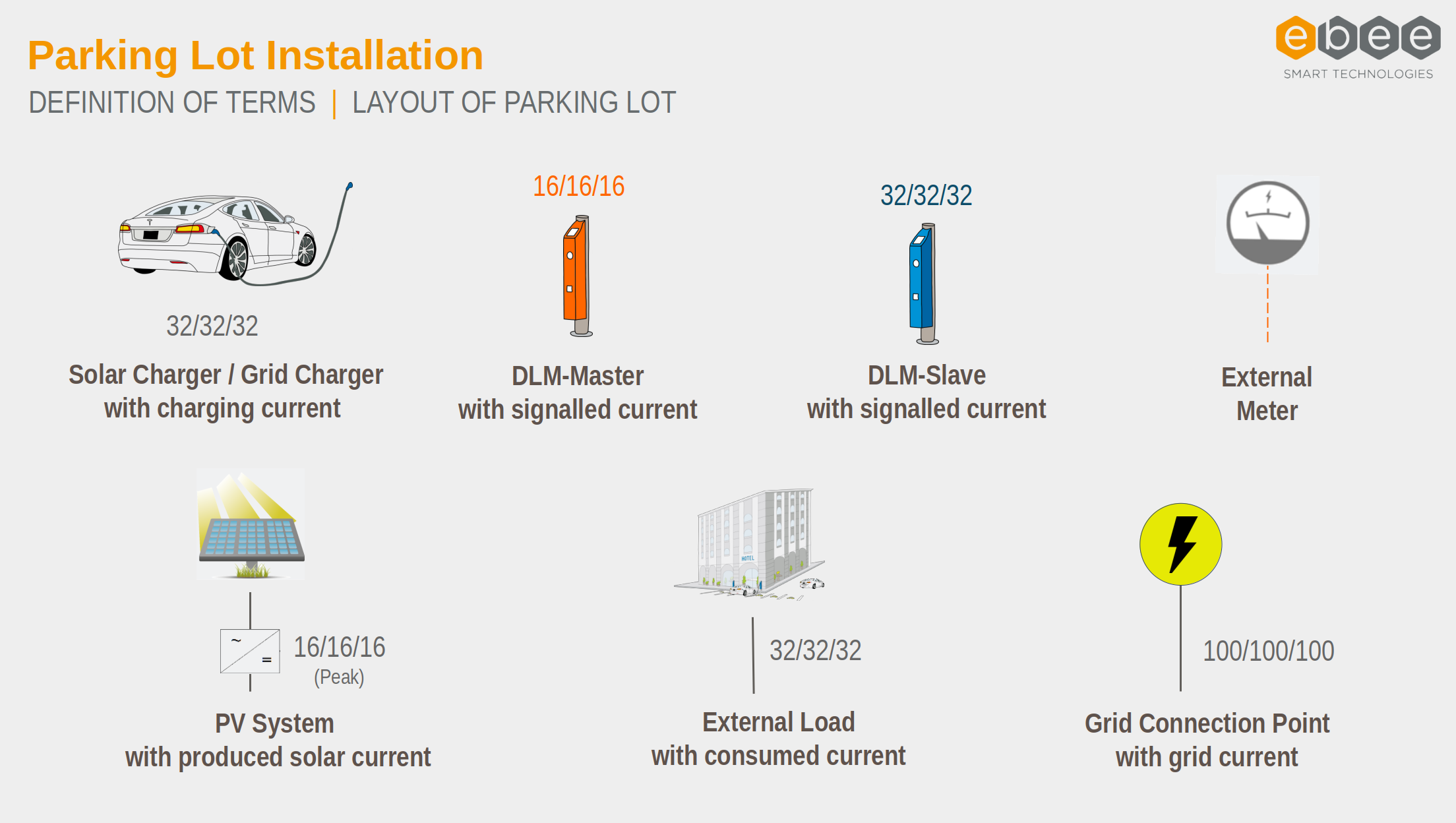
Location Renewable Production
In this configuration, the External Meter is located at the source of renewable energy, e.g., the solar panel. This means that only positive currents are expected at the meter. The measured currents at the external meter directly correlate with the available solar surplus.
Location Grid
Here, the External meter is located at the grid's entry point on the local installation. This means that in a scenario where nothing is being consumed and solar energy is being produced, there would be negative current readings from the external meter as the energy is being fed back into the grid. But there could be positive readings and still have solar current available, for example, when solar current is being used and at the same time, energy is being drawn from the grid.